What is a Cartridge Heater: A Comprehensive Guide
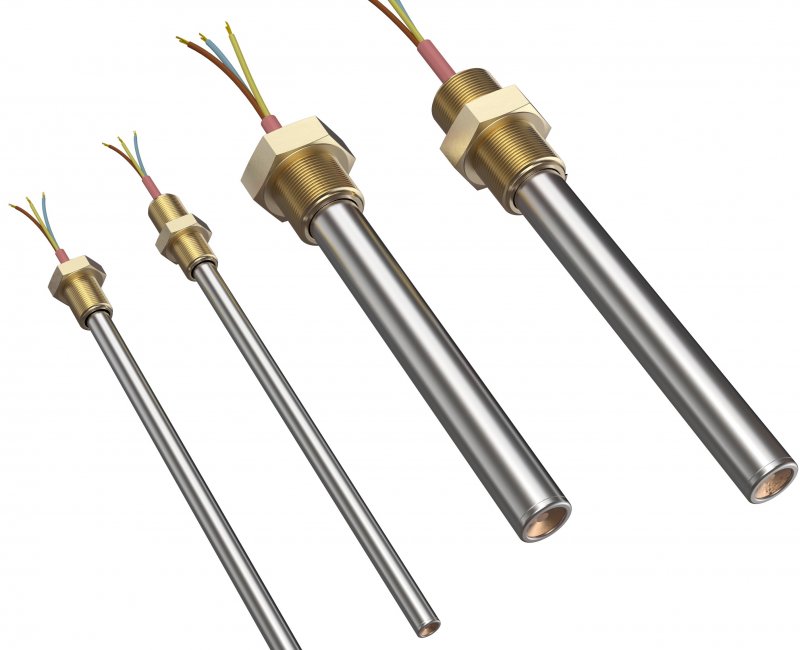
Heating solutions come in various forms, but few are as versatile and efficient as a cartridge heater. These compact powerhouses of heat generation have revolutionized countless industries. Cartridge heaters are crucial in maintaining precise temperatures from manufacturing to food processing. Let’s explore the world of a cartridge heater and its features, applications, and benefits. Understanding Cartridge Heaters Cartridge heaters are cylindrical heating elements designed for insertion into drilled holes or cavities. They provide localized heating in a variety of industrial and commercial applications and are known for their high watt density and ability to transfer heat efficiently. Key Components of a Cartridge Heater Heating Element: Typically made of nickel-chromium resistance wire Insulation: Usually magnesium oxide (MgO) for excellent heat transfer Sheath: Outer metal casing, often stainless steel or Incoloy Lead Wires: For connecting to a power source End Seal: Protects internal components from moisture and contaminants Cartridge heaters are designed to maximize heat transfer while maintaining durability. Their construction allows for efficient heating in confined spaces. How Cartridge Heaters Work The operation of a cartridge heater is based on simple yet effective principles. When an electrical current passes through the resistance wire, it generates heat, which is then transferred through the insulation to the outer sheath. Heat Transfer Process Electrical energy converts to heat in the resistance wire Heat transfers through the insulation to the metal sheath The sheath conducts heat to the surrounding material or medium Types of Cartridge Heaters Cartridge heaters come in various types to suit different applications. Here are some common varieties: Standard Cartridge Heaters: General-purpose heaters for most applications High-Watt Density Cartridge Heaters: For applications requiring intense heat Swaged Cartridge Heaters: Offer improved heat transfer and longer life Miniature Cartridge Heaters: For small spaces and precision heating Customized Cartridge Heaters: Tailored to specific application requirements Applications of Cartridge Heaters The versatility of cartridge heaters makes them suitable for a wide range of industries. Here are some common applications: Plastic Processing: Heating molds and nozzles in injection molding Food Industry: Maintaining temperatures in food processing equipment Medical Equipment: Sterilization and temperature control in medical devices Aerospace: Heating components in aircraft and spacecraft Packaging: Sealing and shrink-wrapping processes Automotive: Engine block heating and component testing 3D Printing: Maintaining precise temperatures for material extrusion Benefits of Using a Cartridge Heater Cartridge heaters offer several benefits that make them popular across industries: Compact Size: Fit easily into small spaces High Watt Density: Provide intense heat in a small package Precise Temperature Control: Allow for accurate heating Durability: Designed to withstand harsh industrial environments Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications Energy Efficiency: Concentrate heat where it’s needed most Easy Installation: Simple to insert and replace Selecting the Right Cartridge Heater Choosing the appropriate cartridge heater is crucial for optimal performance. Consider the following factors: Watt Density: Determine the heat output required Diameter and Length: Ensure proper fit in the application Sheath Material: Choose based on the operating environment Voltage: Match the heater to your power supply Temperature Requirements: Consider maximum operating temperature Special Features: Such as thermocouples or moisture resistance Energy Efficiency and Cost Considerations Cartridge heaters can be an energy-efficient heating solution when used correctly. Here’s why: Targeted Heating: Concentrates heat where it’s needed most Precise Control: Allows for accurate temperature management Quick Heat-Up: Reduces energy waste during warm-up periods Longevity: Quality cartridge heaters have a long operational life While the initial cost of a cartridge heater may be higher than that of some alternatives, its efficiency and longevity often result in long-term cost savings. Wrap Up As heating technology evolves, we expect even more cartridge heater design and functionality innovations. For now, these efficient and reliable heaters remain at the forefront of industrial and commercial heating solutions. Whether you’re considering cartridge heaters for a new application or looking to optimize your current heating processes, these versatile devices offer many benefits. Their ability to provide concentrated, controlled heat in a compact package makes them a valuable tool in our increasingly technology-driven world.
What is a Brass Band Heater: A Comprehensive Guide
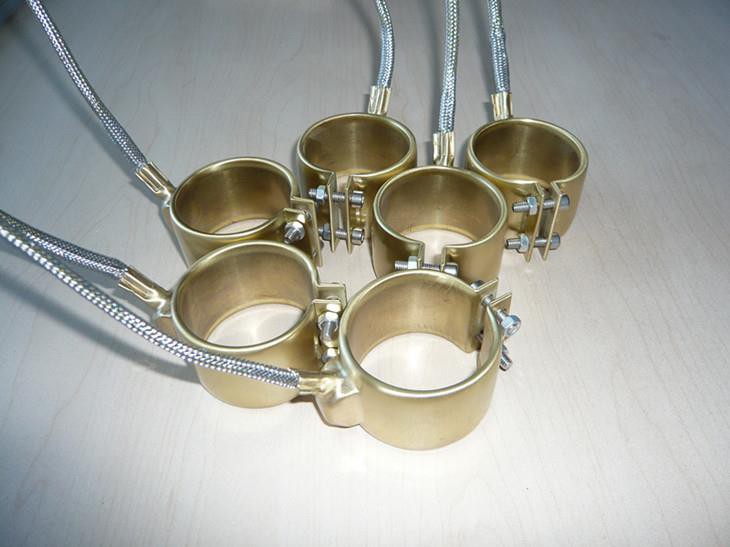

A brass band heater is a versatile and powerful heating solution for industrial efficiency. The device plays a crucial role in countless manufacturing processes, from plastics to food processing. Brass band heaters are the unsung heroes of temperature control. Let’s learn what a brass band heater is and discover its unique features and applications. Understanding Brass Band Heaters Brass band heaters are cylindrical heating elements that wrap around pipes, tubes, or cylinders. They provide uniform heat distribution across their surface and are prized for their excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Key Components of a Brass Band Heater Heating Element: Usually a nickel-chromium wire Brass Sheath: Provides excellent heat transfer and corrosion resistance Insulation: Typically mica or ceramic fiber Terminals: For connecting to a power source Clamping Mechanism: Ensures tight fit around the target surface The brass construction of these heaters offers unique advantages. It allows for rapid heat transfer and uniform temperature distribution. How Brass Band Heaters Work The operation of a brass band heater is based on simple yet effective principles. When electrical current passes through the heating element, it generates heat, which is then transferred through the insulation to the brass sheath. Heat Transfer Process Electrical energy converts to heat in the resistance wire Heat transfers through the insulation to the brass sheath The brass sheath conducts heat to the target surface The efficiency of brass band heaters lies in their ability to provide even heating. This makes them ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control. Types of a Brass Band Heater Brass band heaters come in various types to suit different applications. Here are some common varieties: Standard Brass Band Heaters: General-purpose heaters for most applications High-Watt Density Brass Band Heaters: For applications requiring intense heat Nozzle Brass Band Heaters: Specifically designed for heating injection molding nozzles One-Piece Brass Band Heaters: Offer easy installation and removal Two-Piece Brass Band Heaters: Allow for installation without disconnecting the pipe or cylinder Advantages of Using Brass Band Heaters Brass band heaters offer several benefits that make them popular across industries: Excellent Heat Transfer: Brass conducts heat efficiently Uniform Heating: Provides even temperature distribution Corrosion Resistance: Brass resists corrosion better than many other metals Durability: Designed to withstand harsh industrial environments Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications Easy Installation: Can be easily clamped or bolted into place Energy Efficiency: Concentrates heat where it’s needed most Selecting the Right Brass Band Heater Choosing the appropriate brass band heater is crucial for optimal performance. Consider the following factors: Watt Density: Determine the heat output required Diameter and Width: Ensure proper fit on the target surface Voltage: Match the heater to your power supply Temperature Requirements: Consider maximum operating temperature Special Features: Such as built-in thermocouples or moisture resistance Environmental Factors: Consider any corrosive or abrasive conditions Consulting with a heating specialist can help you select the ideal brass band heater. They can provide guidance based on your specific application needs. Last Word A brass band heater represents a significant advancement in industrial heating technology. Its ability to provide uniform, efficient heating makes it indispensable in many industries. From plastic processing to food production, brass band heaters offer reliable and precise heating solutions. By understanding their principles and applications, you can fully realize the potential of these powerful heating elements.
The Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Heating Elements
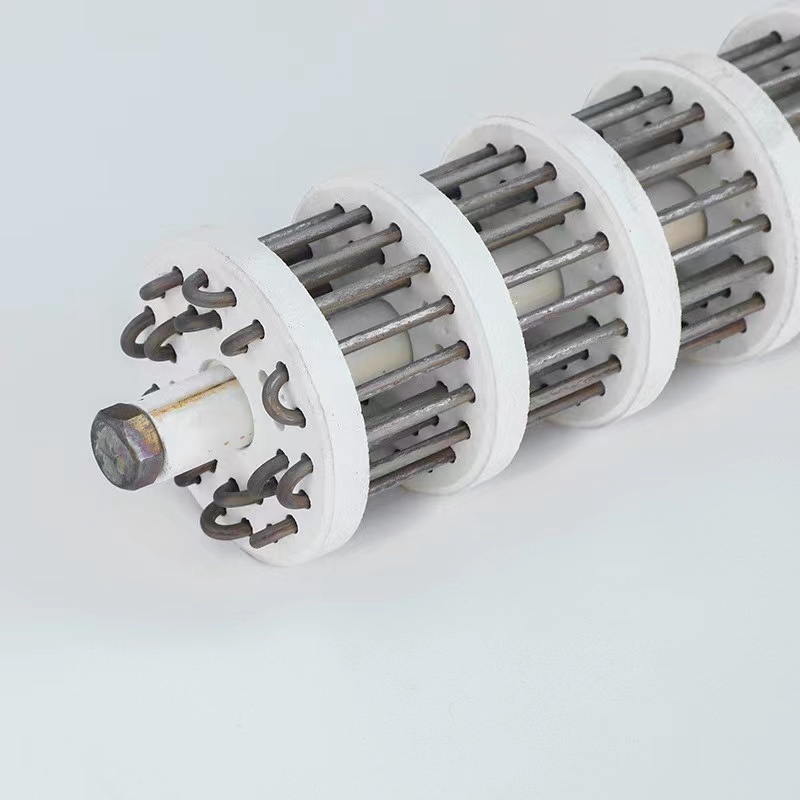

A ceramic heating element, also known as ceramic radiant tube heater, is a type of heating element used in various industrial applications. They are designed to provide efficient and reliable heat transfer, making them a popular choice for many industries. The Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Heating Elements Raw Material Selection The manufacturing process of ceramic heating elements begins with selecting raw materials. Ceramic heating elements are typically made from ceramic powder, metal powder, and other additives. Mixing and Grinding The raw materials are then mixed and ground into a fine powder to ensure uniformity and consistency. Forming The powder mixture is then formed into the desired shape using various techniques such as extrusion, injection molding, or slip casting. Sintering The formed ceramic heating element is then sintered at high temperatures to bond the particles together and achieve the desired density. Coating A metal coating is applied to the ceramic heating element to enhance its thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties. Assembly The ceramic heating element is then assembled into a heating element assembly, which includes a power source, a temperature control system, and other components. Testing and Quality Control The ceramic heating element is then tested for its thermal performance, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength to ensure it meets the required specifications. Types of Ceramic Heating Elements Ceramic Radiant Tube Heater A ceramic radiant tube heater is a type of ceramic heating element that uses a ceramic tube to emit infrared radiation. Ceramic Plate Heaters Ceramic plate heaters are a type of ceramic heating element that uses a ceramic plate to emit heat. Ceramic Strip Heaters Ceramic strip heaters are a type of ceramic heating element that uses a ceramic strip to emit heat. Applications of Ceramic Heating Elements Industrial Heating Ceramic heating elements are commonly used in industrial heating applications such as drying, curing, and annealing. Medical Equipment Ceramic heating elements are used in medical equipment such as surgical instruments, medical implants, and diagnostic devices. Aerospace Ceramic heating elements are used in aerospace applications such as satellite, aircraft, and spacecraft components. Benefits of Ceramic Heating Elements High-Temperature Resistance Ceramic heating elements can withstand extremely high temperatures, making them suitable for high-temperature applications. Corrosion Resistance Ceramic heating elements are corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for harsh environments. Low Maintenance Ceramic heating elements require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective option for many applications. Wrap Up In conclusion, the manufacturing process of ceramic heating elements involves several stages, from raw material selection to testing and quality control. Ceramic heating elements are used in various industrial applications and offer several benefits, including high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance. By understanding the manufacturing process and applications of ceramic heating elements, you can make informed decisions when selecting the right heating element for your specific needs.
Cartridge Heater For 3d Printer: A Comprehensive Guide

Are you tired of dealing with inconsistent temperature control in your 3D printing process? Do you struggle with hot-ends that take forever to heat up or cool down? Look no further! In this article, we’ll explore the benefits, types, and applications of cartridge heaters for 3D printers. What is a Cartridge Heater? A cartridge heater is a heating element designed specifically for 3D printing applications. It’s a self-contained unit that consists of a heating coil, insulation, and a thermally conductive material, all housed within a compact cartridge. This design allows for efficient heat transfer, precise temperature control, and fast heating and cooling times. Benefits of Cartridge Heaters for 3D Printers Improved Temperature Control Cartridge heaters offer superior temperature control compared to traditional heating elements. With a cartridge heater, you can achieve precise temperature settings and maintain them consistently throughout printing. Faster Heating and Cooling Times Cartridge heaters can heat up and cool down quickly, reducing printing time and increasing productivity. Increased Safety The self-contained design of cartridge heaters eliminates the risk of electrical shock and reduces the risk of fires. Compact Design Cartridge heaters are designed to be compact, making them ideal for use in 3D printers with limited space. Types of Cartridge Heaters for 3D Printers Resistance Wire Cartridge Heaters Resistance wire cartridge heaters generate heat using a resistive heating element. They’re suitable for applications that require high temperatures and are often used in extruders and hot-ends. Ceramic Cartridge Heaters Ceramic cartridge heaters generate heat using a ceramic heating element. They’re suitable for applications that require high temperatures and are often used in extruders and hot-ends. PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) Cartridge Heaters PTC cartridge heaters use a PTC heating element to generate heat. They’re suitable for applications that require precise temperature control and are often used in extruders and hot-ends. Applications of Cartridge Heaters for 3D Printers Extruders Cartridge heaters are commonly used in extruders to heat the filament to the optimal temperature for printing. Hotends Cartridge heaters are used in hot-ends to heat the nozzle to the optimal temperature for printing. Print Bed Cartridge heaters can heat the print bed to the optimal temperature for printing. Chamber Heating Cartridge heaters can heat the printing chamber to the optimal temperature for printing. How to Choose the Right Cartridge Heater for Your 3D Printer Consider the Temperature Range Choose a cartridge heater that can achieve the desired temperature range for your printing application. Consider the Power Consumption Choose a cartridge heater that consumes the right amount of power for your printing application. Consider the Size and Compatibility Choose a cartridge heater that fits your 3D printer’s hotend or extruder and is compatible with your printing software. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Cartridge Heaters for 3D Printers Overheating Check the temperature setting and adjust it accordingly. Ensure proper airflow and cooling around the cartridge heater. Underheating Check the power consumption and adjust it accordingly. Ensure proper insulation and thermal conductivity around the cartridge heater. Noise and Vibration Check the cartridge heater’s installation and ensure it’s properly secured. Check for any loose connections or worn-out components. Conclusion Cartridge heaters for 3D printers offer improved temperature control, faster heating and cooling times, increased safety, and compact design. By understanding the benefits, types, and applications of cartridge heaters, you can make an informed decision when choosing the right one for your 3D printing needs. Remember to consider the temperature range, power consumption, size, and compatibility when selecting a cartridge heater. With the right cartridge heater, you can achieve optimal printing results and take your 3D printing game to the next level.










