High Temperature Cable the Complete 2025 Expert Guide
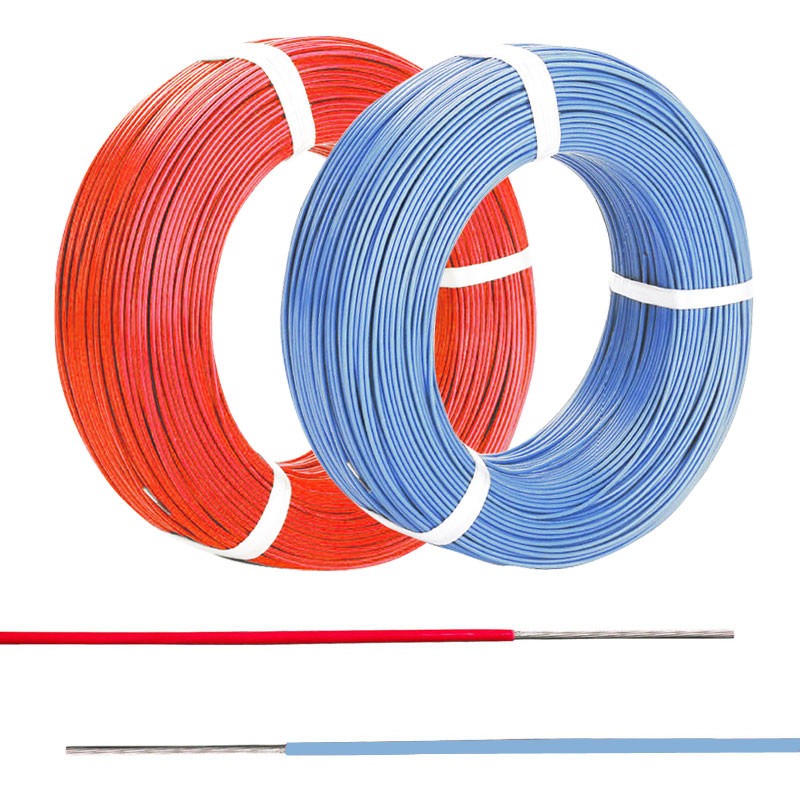
Let’s face it heat is one of the biggest enemies of electrical systems. Whether it’s a blazing factory floor, a roaring furnace, or an industrial oven operating around the clock, regular cables just can’t survive in these harsh environments. That’s exactly where high temperature cables step in like unsung heroes. What Is a High Temperature Cable? A high temperature cable is a specially engineered electrical wire designed to operate safely and reliably under extreme heat. Unlike regular wires that start breaking down at 80–105°C, these cables can handle temperatures ranging from 150°C to over 1000°C, depending on materials and design. Think of them as heat-proof armor for your electrical systems. Why High Temperature Resistance Matters When ordinary cables face excessive heat, their insulation melts, cracks, or becomes brittle leading to short circuits, power loss, fires, and expensive downtime. High temperature cables prevent all that chaos. They maintain electrical stability even when the heat is relentless, ensuring safety and uninterrupted performance. How High Temperature Cables Work At first glance, a cable might seem simple, but inside, it’s a carefully engineered system designed to survive extreme conditions. Core Electrical Structure The heart of any cable is its conductor, usually copper or nickel-plated copper. This ensures smooth electrical flow even under continuous heat. High temperature conductors are designed to minimize resistance fluctuations due to heat expansion. Insulation vs Jacket Key Differences Insulation protects the conductor from short circuits. Outer jacket shields the cable from mechanical damage, chemicals, oils, and environmental hazards. In high temperature cables, both layers are made from materials that resist thermal breakdown. Heat Transfer and Electrical Stability These cables slow down heat transfer toward the conductor and prevent electrical leakage. This balance keeps voltage stable even in scorching environments kind of like thermal insulation for your electricity. Types of High Temperature Cables Different industries demand different heat resistance levels. Here are the most popular types you’ll encounter: Silicone Rubber Cables These cables handle temperatures up to 200–250°C. They’re extremely flexible and ideal for dynamic environments like robotics, conveyor systems, and heating appliances. PTFE (Teflon) High Temperature Cables PTFE cables can withstand up to 260°C continuously and even higher peaks. They offer outstanding chemical resistance and are commonly used in chemical plants, aerospace, and medical equipment. Fiberglass Insulated Cables Designed for 400–500°C, fiberglass cables are often found in furnaces, kilns, and steel plants. They resist flames but require protective coatings for moisture resistance. Mica Insulated Cables For extreme temperatures reaching 1000°C, mica-insulated cables dominate. These are used in fire survival circuits, emergency power systems, and heavy industries. Materials Used in High Temperature Cables Materials determine everything from heat resistance to flexibility and lifespan. Conductors Bare copper Tin-plated copper Nickel-coated copper Nickel conductors are preferred for ultra-high heat environments. Insulation Materials Silicone rubber PTFE (Teflon) Fiberglass Mica tape Ceramic compounds Each insulation type offers a unique balance between heat resistance and flexibility. Outer Sheathing Outer jackets protect against: Abrasion Oil Chemicals UV radiation Mechanical stress Common sheath materials include fluoropolymers, braided fiberglass, and silicone compounds. Temperature Ratings Explained Not all heat resistance is created equal. Low vs Medium vs Extreme Heat Levels 150–200°C: Home appliances and light industrial use 250–400°C: Heavy manufacturing equipment 500–1000°C: Steel plants, furnaces, emergency systems Continuous vs Peak Temperature Ratings Continuous rating: Safe long-term operating temperature Peak rating: Maximum heat the cable can tolerate briefly Ignoring these limits can shorten cable life drastically. Industrial Applications of High Temperature Cables These cables are everywhere high heat exists. Manufacturing & Automation Robotic arms, molding machines, and automated systems constantly face heat from motors and friction. High temperature cables keep the power flowing without failure. Power Plants From boilers to turbines, thermal power plants depend heavily on heat-resistant wiring to avoid catastrophic breakdowns. Steel & Foundry Industry Few environments are harsher than molten metal operations. High temperature cables ensure uninterrupted control and safety circuits. Plastic & Rubber Processing Extruders, injection molding machines, and hot runner systems rely on precise temperature control made possible by heat-resistant cables. High Temperature Cables in Household & Commercial Use Not everything high-temp is industrial. These cables also quietly power your daily life. Ovens and Heating Appliances Electric ovens, geysers, heaters, and stoves require wiring that won’t burn under constant heat exposure. HVAC Systems Heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning units push wiring to its thermal limits—especially in commercial buildings. Lighting and Electrical Panels High-wattage lighting systems and control panels often rely on heat-resistant wiring to avoid insulation failure. Advantages of High Temperature Cables Why not just use regular cables and replace them often? Because that approach costs more in the long run. Safety Heat-resistant insulation drastically reduces fire risk, electrical shorts, and system failures. Longevity These cables last 2–5 times longer than standard wires in hot environments. Less replacement equals less downtime. Electrical Stability They maintain voltage integrity under thermal stress, ensuring consistent machine performance. Disadvantages & Limitations No technology is perfect. Cost Factors High temperature cables cost more upfront due to premium materials and complex manufacturing. Installation Challenges Some high-temp cables, especially fiberglass and mica types, require special handling during installation to avoid damage. High Temperature Cable vs Regular Cable Still unsure which one you need? Let’s make it clear. Performance Comparison Feature Regular Cable High Temp Cable Max Heat 80–105°C 150–1000°C Safety Moderate Very High Lifespan in Heat Short Long Cost Low Medium to High Cost vs Value While high temperature cables cost more initially, they save huge amounts on maintenance, downtime, and fire risk. How to Select the Right High Temperature Cable Choosing the wrong cable is like wearing winter clothes in a desert doesn’t end well. Temperature Range Know your operating temperature and always select a cable rated 20–30% higher than your maximum heat. Chemical Resistance If your environment has oils, acids, or solvents, choose fluoropolymer or silicone jackets. Flexibility & Mechanical Strength Dynamic applications require flexible insulation, while static installs can use rigid, high-strength sheathing. Installation Best Practices Even the best cable can fail if installed poorly. Cable Routing Tips Avoid sharp
Cartridge Heater Manufacturer Complete Industry Guide
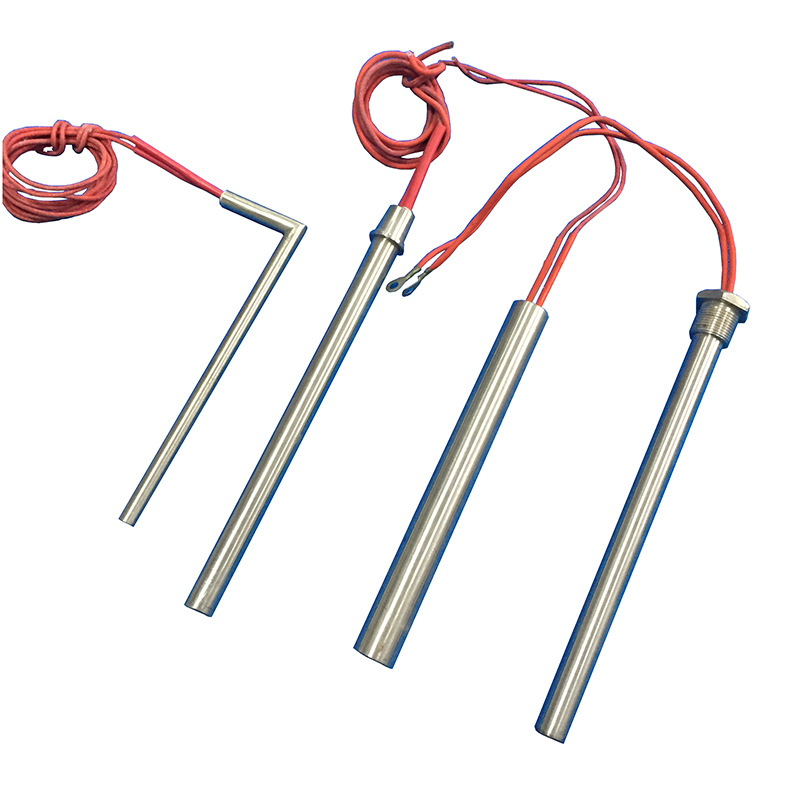

In today’s fast-moving industrial world, heat plays a silent yet powerful role. From plastic molding to medical equipment, nothing runs smoothly without controlled heating. And right at the heart of these heating systems sits an unsung hero the cartridge heater. If you’ve ever wondered what a cartridge heater manufacturer really does and why this industry is growing so rapidly, you’re in the perfect place. Let’s break it all down in a simple, real-world way no boring technical overload, just useful, practical knowledge. What Is a Cartridge Heater? Think of a cartridge heater as a compact, powerful electric heater packed into a metal tube. It’s designed to slide right into drilled holes and deliver intense, focused heat exactly where it’s needed. Basic Working Principle A cartridge heater works by converting electrical energy into heat using a resistance wire coiled inside a metal sheath. Once powered, it heats up rapidly and transfers that heat directly into the surrounding material. Key Features of Cartridge Heaters High temperature resistance Compact and space-saving Fast heat-up time Extremely durable Role of a Cartridge Heater Manufacturer A cartridge heater manufacturer does much more than just “make heaters.” They engineer heat solutions. Design & Engineering Manufacturers calculate proper watt density, voltage, and dimensions based on end-use. Every heater is designed for performance and safety. Material Selection Premium stainless-steel sheaths, high-purity magnesium oxide insulation, and top-grade resistance wire ensure longevity and efficiency. Quality Control From resistance testing to insulation checks, every heater undergoes strict inspections before leaving the facility. Types of Cartridge Heaters Different industries demand different heat strengths so manufacturers produce several types. High-Density Cartridge Heaters Used in extreme temperature applications like plastic molds and die casting. Low-Density Cartridge Heaters Ideal for softer materials where gentle, even heating is needed. Miniature Cartridge Heaters Perfect for compact applications like medical devices and lab instruments. Square Cartridge Heaters Used when round heaters are not suitable for tight or flat surface installations. Key Components Used in Cartridge Heaters Every cartridge heater is built like a carefully layered sandwich. Heating Wire Usually made from nickel-chromium alloy for maximum heat resistance. Magnesium Oxide Insulation This powder ensures fast heat transfer while keeping electricity safely insulated. Stainless Steel Sheath Acts like armor protecting the heater from corrosion and mechanical damage. Manufacturing Process of Cartridge Heaters This is where the magic happens. Coil Winding Resistance wire is precisely wound to achieve uniform heating. Insulation Filling Magnesium oxide powder is packed around the coil for thermal conductivity. Swaging Process The heater is compressed under high pressure to remove air gaps and improve heat transfer. Sealing & Testing Ends are sealed, leads attached, and each unit is electrically tested for safety. Industries That Use Cartridge Heaters Cartridge heaters power countless industries without anyone even noticing. Plastic & Injection Molding They heat mold cavities to shape plastic parts perfectly. Packaging Industry Used in sealing machines for shrink wrapping and heat sealing. Medical Equipment Autoclaves, sterilizers, and diagnostic devices rely on precise heat. Food Processing From ovens to warmers, consistent heating keeps food safe and tasty. Importance of Custom Cartridge Heaters One-size-fits-all doesn’t work in industrial heating. Custom Diameters & Lengths Manufacturers build heaters to exact hole sizes for perfect fit. Watt Density Customization Different materials require different heating intensity. Voltage Customization From 12V to 480V manufacturers tailor heaters to power systems worldwide. Global Demand for Cartridge Heater Manufacturers The world is heating up industrially speaking. Growth in Automation More machines mean more heaters simple math. Rise of Smart Factories Modern industries want precise, responsive heating systems, driving demand upward. How to Choose the Right Cartridge Heater Manufacturer Not all manufacturers are created equal. Experience & Certification Look for ISO-certified manufacturers with proven industry experience. Custom Manufacturing Capabilities A good manufacturer can design to your exact specs. After-Sales Support Heaters are long-term investments. Technical support matters. Quality Standards in Cartridge Heater Manufacturing Good heaters follow strict quality rules. ISO Certifications Ensure process control and consistency. Electrical Safety Standards Guarantee shock protection, insulation strength, and reliable terminals. Advantages of Buying from a Professional Manufacturer Why risk cheaper, unreliable options? Longer Heater Life Premium materials equal longer operational life. Energy Efficiency Proper design reduces power consumption and heat loss. Application-Specific Performance Heaters engineered for your application work smarter not harder. Common Problems Solved by Cartridge Heaters These small heaters solve big industrial headaches. Uneven Heating Cartridge heaters deliver uniform temperature distribution. Slow Heat-Up Times They reach target temperatures quickly and efficiently. Energy Wastage Direct-contact heating minimizes energy loss. Future Trends in Cartridge Heater Manufacturing The future of heating is smarter and greener. Smart Heating Solutions Sensor-integrated heaters are entering the market. Energy-Efficient Designs Lower power consumption with higher heating efficiency is the goal. Why Local vs International Cartridge Heater Manufacturers Matter Choosing between local and overseas suppliers affects your business. Pricing Difference International options may be cheaper but hidden costs add up. Delivery Time Local manufacturers offer faster turnaround. Technical Support On-site support gives local manufacturers a strong advantage. Environmental Impact & Sustainability Modern manufacturers are going green. Eco-Friendly Materials Recyclable metals and safer insulation materials are being adopted. Low Energy Consumption High-efficiency heaters reduce carbon footprints significantly. Conclusion Choosing the right cartridge heater manufacturer is not just about buying a product it’s about investing in performance, safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability. Whether you’re in plastic molding, medical equipment, food processing, or automation, a high-quality cartridge heater can make the difference between smooth production and constant breakdowns. As industries continue to evolve and automation grows stronger, cartridge heaters will only become more essential. Working with an experienced, certified manufacturer ensures that your heating solutions are built to last, save energy, and deliver consistent results day after day. FAQs What is the average lifespan of a cartridge heater?With proper installation and usage, a high-quality cartridge heater can last anywhere from 3 to 7 years. Can cartridge heaters be custom-made?Yes, manufacturers offer full customization in terms of size, voltage, watt density, and lead options. Are cartridge heaters energy efficient?Absolutely. Their direct-contact heating










