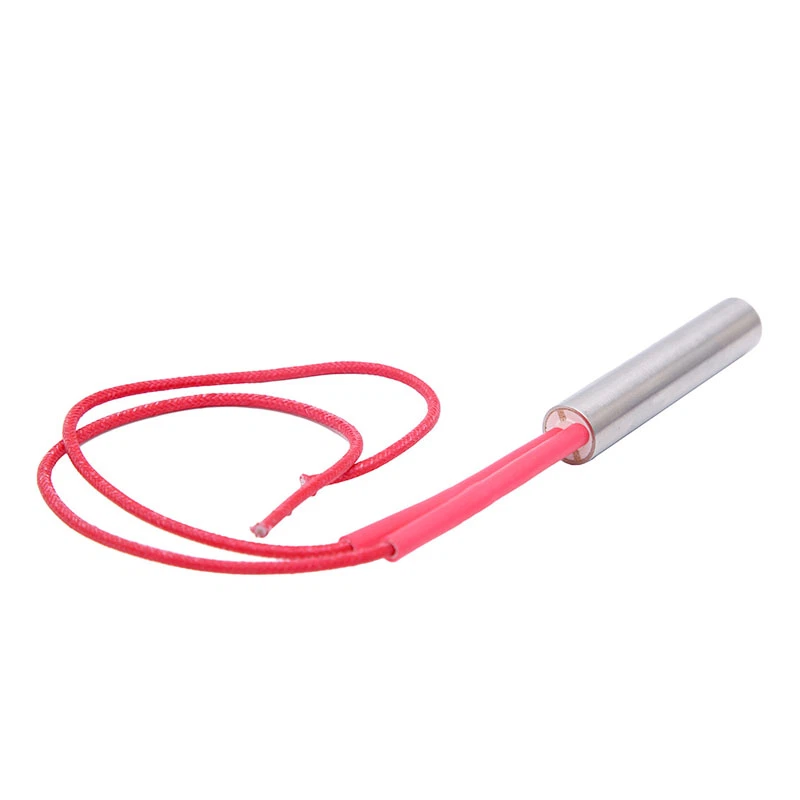
A DC cartridge heater plays a critical role in compact and precise heating applications. It delivers controlled, localized heat directly to solid metal parts, plastic molds, or metal dies.
Built for reliability and efficiency, the 12-volt variant is especially suited for small-scale or mobile operations where AC power is unavailable or unsuitable.
When 12V DC power is applied, electrical energy flows through the resistance coil, converting to thermal energy due to the Joule heating effect (I²R losses). The generated heat transfers outward through the magnesium oxide (MgO) insulation to the metal sheath, and then into the surrounding solid medium via conduction.
The design ensures rapid heat-up times and consistent surface temperatures, typically ranging between 100°C to 800°C depending on the watt density and thermal load.
Key technical characteristics:
- Voltage rating: 12V DC, compatible with battery packs and solar-powered systems
- Wattage: Typically ranges from 25W to 250W for small-diameter heaters (e.g., 6.5mm to 12.5mm)
- Watt density: Can reach up to 50–100 W/cm² depending on the application and material fit
- Tolerance: Diameters are precision-ground to +0.02/-0.00 mm for optimal bore fit
- Sheath materials: Commonly 304 or 316 stainless steel for thermal stability and corrosion resistance
- Insulation resistance: >100 MΩ at 500VDC, ensuring electrical isolation
- Leakage current: Typically under 0.5 mA at operating voltage
Key Applications of a 12 Volt DC Cartridge Heater
Industries rely on DC cartridge heaters for several critical applications, including:
- 3D printing – maintaining consistent nozzle temperature
- Medical devices – precise heating in sterilization tools or diagnostic equipment
- Automotive – heating fluids, battery enclosures, or dies in low-voltage systems
- Battery-powered machinery – such as drones or mobile soldering tools
- Portable scientific instruments – where AC power isn’t practical
Each application requires consistent, localized heat that a 12V DC cartridge heater delivers without thermal overshoot.
Why Choose a 12 Volt Configuration?
The 12-volt rating isn’t arbitrary. It directly aligns with low-voltage system demands:
- Safe for use with battery-powered devices
- Compatible with solar-based or off-grid systems
- Reduces risk of electrical hazards in mobile setups
- Provides precise thermal control without overloading small circuits
- Ideal for environments where AC power introduces interference
While the heat output depends on watt density and sheath material, a 12V DC cartridge heater offers efficient energy transfer at a manageable power load.
Construction That Supports Precision Heating
The internal structure directly affects performance. Most heaters include:
- High-resistance coil wound for uniform heat distribution
- Ceramic or magnesium oxide (MgO) insulation for heat retention and electrical isolation
- Stainless steel sheath for corrosion resistance and thermal conduction
- Lead wires insulated with fiberglass or Teflon for high-heat environments
This construction ensures long life, efficient heat transfer, and safe operation even under demanding conditions.
Performance Factors That Matter
Several parameters influence how well a 12V DC cartridge heater performs:
- Watt Density – heat output per square inch; higher densities heat faster but need tighter control
- Insertion Fit – close tolerance between heater and bore enhances conduction
- Material Type – metal types like aluminum or steel absorb heat at different rates
- Control Systems – pairing with thermostats or PID controllers ensures accuracy
Selecting the correct heater means understanding both thermal needs and electrical constraints.
Final Thoughts
In summary, a 12-volt DC cartridge heater functions as a precision thermal component for energy-efficient, low-voltage systems that require controlled, focused heat in restricted spaces. It integrates seamlessly with modern compact equipment, delivering consistent performance with minimal power draw.