3D printing has changed the way we create objects. At the heart of this technology lies a crucial component – the heater. A 3D printer heater manufacturer plays a key role in the quality and efficiency of 3D prints. This blog post will uncover seven essential facts about 3D printer heaters that every enthusiast and professional should know.
1. The Role of Heaters in 3D Printing
3D printer heaters are the unsung heroes of the printing process. They melt the plastic filament, turning it into a liquid that can be shaped into amazing 3D objects. Without proper heating, your prints would be weak, brittle, or might not even form at all.
Heaters work in two main areas of a 3D printer:
- The extruder: This is where the plastic filament is melted.
- The print bed: This keeps the printed object warm to prevent warping.
The right temperature is crucial. Too hot, and your plastic might burn or lose its properties. Too cold, and it won’t stick together well. That’s why understanding heaters is so important for successful 3D printing.
2. Types of 3D Printer Heaters
There are several types of heaters used in 3D printers. Each has its own strengths and best uses:
- Cartridge Heaters: These are the most common. They’re small, cylindrical, and fit snugly into the heater block.
- Ceramic Heaters: These heat up quickly and evenly. They’re often used in high-end printers.
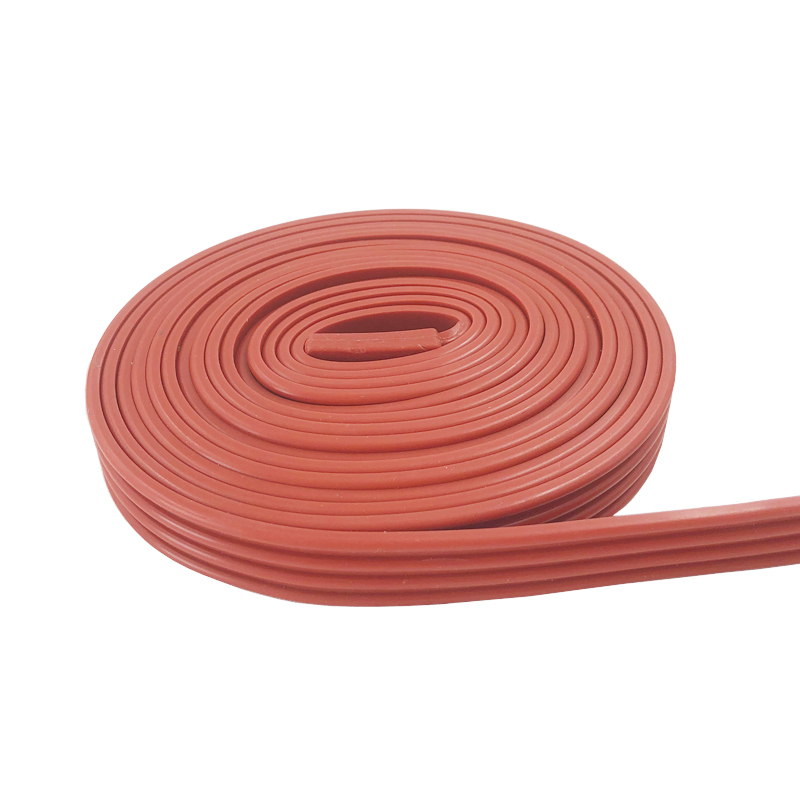
- Silicone Heaters: These are flat and flexible. They’re great for heating print beds.
- Induction Heaters: These use electromagnetic fields to heat metal. They’re fast but more complex.
- Nichrome Wire: This is a resistive wire that heats up when electricity flows through it.
Choosing the right type depends on your printer design and what you’re printing. Some materials need higher temperatures, while others work best with steady, lower heat.
3. The Impact of Heater Quality on Print Results
The quality of your 3D printer heater can make or break your prints. High-quality heaters from reputable manufacturers offer several benefits:
- Consistent Temperature: They maintain a steady temperature, which is crucial for print quality.
- Fast Heating: Good heaters reach the desired temperature quickly, saving you time.
- Durability: They last longer, saving you money and hassle in the long run.
- Safety: Quality heaters have built-in safety features to prevent overheating.
Poor quality heaters can lead to:
- Uneven heating
- Temperature fluctuations
- Slow warm-up times
- Premature failure
Investing in a good heater can significantly improve your 3D printing results. It’s not just about the initial cost – think about the long-term benefits and the quality of your prints.
4. Temperature Control and Its Importance
Precise temperature control is vital in 3D printing. Different materials need different temperatures:
- PLA: 180-230°C
- ABS: 210-250°C
- PETG: 230-250°C
- Nylon: 240-260°C
These temperatures aren’t just suggestions. They’re critical for proper melting and layer adhesion. Modern 3D printers use thermistors or thermocouples to measure temperature. These sensors work with the printer’s control board to maintain the right heat.
Good temperature control also affects:
- Layer Adhesion: Proper heat ensures layers stick together well.
- Warping: Correct bed temperature prevents the base of prints from curling up.
- Surface Finish: The right temperature gives smoother, more professional-looking prints.
Advanced printers even allow for temperature changes during printing. This can help with complex shapes or multi-material prints.
5. Energy Efficiency and Power Consumption
3D printing can use a lot of energy, especially for long prints. Heaters are often the biggest power consumers in a 3D printer. Here’s why efficiency matters:
- Cost: More efficient heaters mean lower electricity bills.
- Environmental Impact: Less energy use is better for the planet.
- Print Time: Efficient heaters warm up faster, reducing overall print time.
Some ways to improve efficiency:
- Insulation: Good insulation around the heater block and print bed reduces heat loss.
- PID Tuning: This adjusts how the printer controls the heater, optimizing power use.
- Smart Power Management: Some printers reduce power to heaters when not in use.
Modern 3D printer heater manufacturers are focusing on creating more efficient heating systems. This not only saves energy but also improves print quality by maintaining more stable temperatures.
6. Maintenance and Longevity of 3D Printer Heaters
Like any part of a 3D printer, heaters need care to last. Proper maintenance can extend the life of your heater and improve print quality. Here are some tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Remove any plastic buildup around the heater block.
- Check Connections: Loose wires can cause temperature fluctuations or failures.
- Monitor Performance: Watch for signs of inconsistent heating or longer warm-up times.
- Replace Thermistors: These sensors can wear out over time, affecting temperature accuracy.
Signs that your heater might need replacement:
- Inconsistent temperatures
- Difficulty reaching or maintaining temperature
- Visible damage to the heater or its wires
Most heaters last for hundreds or even thousands of hours of printing. But their lifespan can vary based on usage and quality. Keeping spare heaters on hand can prevent long downtimes if a replacement is needed.
7. Future Trends in 3D Printer Heater Technology
The world of 3D printing is always advancing, and heater technology is no exception. Here are some exciting trends to watch:
- Faster Heating: New materials and designs are allowing for quicker warm-up times.
- More Precise Control: Advanced algorithms are improving temperature stability.
- Multi-Zone Heating: Some printers now use multiple heaters for more complex temperature control.
- Smart Heaters: IoT-enabled heaters that can be monitored and controlled remotely.
- Energy Harvesting: Some researchers are exploring ways to capture and reuse heat energy in 3D printers.
- New Materials: Heaters designed for exotic filaments that require very high or precise temperatures.
- Miniaturization: As 3D printers get smaller, heaters are shrinking too, without losing efficiency.
These advancements promise to make 3D printing faster, more efficient, and capable of working with an even wider range of materials.
Final Words
3D printer heaters are a critical component that often doesn’t get the attention it deserves. Understanding these seven facts can help you choose the right printer, maintain it properly, and get the best results from your 3D printing projects. As technology continues to advance, we can look forward to even more impressive capabilities from these essential parts.